Modern cars can travel very fast, so good brakes are essential for saftey. Practically most modern cars have disc brakes on the front wheels, and drum brakes on the rear wheels.
Disc Brakes
The most common type of disc brake on modern cars is the single-piston floating caliper.
The main components of a disc brake are:
l The brake pads
l The caliper, which contains a piston
l The rotor, which is mounted to the hub
The disc brake is a lot like the brakes on a bicycle. Bicycle brakes have a caliper, which squeezes the brake pads against the wheel. In a disc brake, the brake pads squeeze the rotor instead of the wheel, and the force is transmitted hydraulically instead of through a cable. Friction between the pads and the disc slows the disc down.
A moving car has a certain amount of kinetic energy, and the brakes have to remove this energy from the car in order to stop it. How do the brakes do this? Each time you stop your car, your brakes convert the kinetic energy to heat generated by the friction between the pads and the disc. Most car disc brakes are vented.
Vented disc brakes have a set of vanes, between the two sides of the disc, that pumps air through the disc to provide cooling.
Drum Brakes
Drum brakes work on the same principle as disc brakes:Shoes press against a spinning surface. In this system, that surface is called a drum.
In the drum-and-shoe type, there is a wheel brake cylinder with two pistons. When brake pedal is pushed by the driver, brake fluid is forced into the brake cylinder by the action at the master cylinder, and the two pistons are forced outward. This causes the curved brake shoes to move into contact whith the brake drum. The brake shoes apply friction to the brake drum, forcing it and the wheel to slow or stop.
Many cars have drum brakes on the rear wheels and disc brakes on the front. Drum brakes have more parts than disc brakes and are harder to service, but they are less expensive to manufacture, and they easily incorporate an emergency brake mechanism.
Power Brakes
Back in the day, when most cars had drum brakes, power brakes were not really necessary-drum brakes naturally provide some of their own power assist. Since most cars today have disc brakes, at least on the front wheels, they need power brakes. Without this device, a lot of drivers would have very tired legs.
The brake booster uses vacuum from the engine to multiply the force that your foot applies to the master cylinder.
Anti-Lock Braking Systems (ABS)
Anti-Lock Braking Systems (ABS) is designed to provide best deceleration and stability during hard braking by adjusting the hydraulic pressure at each wheel to prevent wheel lock.
There are many different variations and control algorithms for ABS systems. Regardless of the type, all work in a similar manner.
The controller monitors the speed sensors at all times. It is looking for decelerations in the wheel that are out of the ordinary. Right before a wheel locks up, it will experience a rapid deceleration. If left unchecked, the wheel would stop much more quickly than any car could. It might take a car five seconds to stop from 60 mph (96.6 kph) under ideal conditions, but a wheel that locks up could stop spinning in less than a second.
The ABS has been designed with Self Diagnostic Capability. There are two self checks that the system performs every time the vehicle is started. First, when the key is turned on, the system performs an electrical check called Start-Up. During this check, the Red Brake Warning Lamp and the Anti-lock Warning Lamp are illuminated. Then turned off at the end of the test, after about 1 to 2 seconds. When the vehicle reaches a speed of about 4.8 to 6.4 km per hour, the system performs a functional check called Drive-Off, hydraulic valves are activated briefly to test their function. Drive-Off can be detected as a series of rapid clicks upon driving off the first time the car is started. If the brake pedal is applied during Drive-Off, the test by-passed. Both of these conditions are a normal part of the system self test. Most fault cnditions will set a ABS Fault code in the CAB (controller anti-lock brake), which can be retrieved to aid in fault diagnosis.
参考译文:
现代汽车速度很快,良好的制动系统式安全的基本保证。实际上,大都数汽车的前轮采用盘式制动,后轮采用鼓式制动。
盘式制动器
 nload="javascript:if(>740)=740" align=center border=0>
nload="javascript:if(>740)=740" align=center border=0>
现代汽车中常见的是盘式制动器是盘式制动器。
盘式制动器包括以下主要的零件:
制动摩擦片
制动钳,内活塞
制动盘,安装在轮毂上
盘式制动器和自行车上的刹车很像。自行车的刹车有一个夹钳,夹钳加紧摩擦片,使它紧紧地夹紧车轮。在盘式制动器中,摩擦片夹住的是制动盘而不是车轮,夹紧力不是通过刹车带提供的而是液压系统提供的制动力。制动摩擦片和盘之间的摩擦力使制动盘速度降下来。
行驶中的车辆具有一定得动能,因此,制动系统必须消耗掉车的动能才能使车停住。
制动器是如何消耗能量的呢?每当你停车的时候,摩擦片和制动盘之间的摩擦就把动能转变成了热能。大多数汽车的制动器是通风的。
通风盘式制动器的两侧有叶片,空气在泵的作用下流动使制动盘冷却。
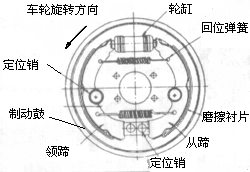
鼓式制动器
 nload="javascript:if(>740)=740" align=center border=0>
nload="javascript:if(>740)=740" align=center border=0>
鼓式制动器与盘式制动器的工作原理是一样的:制动蹄压在旋转表面上。在鼓式制动中,这个表面被称为鼓。
在蹄-鼓制动器中,有一个带有两个活塞的制动轮缸。当驾驶员踩下制动踏板时,制动液由于主缸的作用进入轮缸,推动两个活塞向外侧移动。这使得圆弧状的制动蹄张开与制动鼓相接触。制动蹄对制动鼓所产生的摩擦力迫使制动鼓和车轮减速或停车。
很多车子在后轮采用鼓式制动,前轮采用盘式制动。鼓式制动必盘式制动的零件多,维护也更困难,但是鼓式制动器造价便宜,且易于与紧急制动机构配合。
制动助力器
目前,后轮大部分采用鼓式制动,不一定需要动力制动——鼓式制动可以自己提供助力。因为现在大多数汽车采用盘式制动,至少前轮采用盘式制动,那就需要动力制动了。没有制动助力器的话,那么驾驶员的腿部会很疲劳。
制动助力器采用真空泵把你的脚作用在主缸上的力放大。
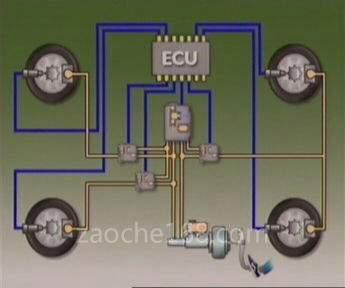
车轮放抱死制动系统(ABS)
 nload="javascript:if(>740)=740" align=center border=0>
nload="javascript:if(>740)=740" align=center border=0>
放抱死制动系统(ABS)是为汽车急刹车时提供最佳减速度和稳定性而设计的,它通过调节每个车轮的制动液压来防止车轮抱死。
目前有各种各样的ABS系统以及控制。不考虑其类型,所有系统的工作原理是相似的。
控制系统始终监视着速度传感器。它随时检测车轮的减速度是否正常。当车轮即将抱死前,ABS系统迅速检测到车轮减速异常。假如没有ABS系统的检测,那么抱死比车轮普通制动更迅速。在理想条件下,当车速为每小时60英里行驶时,完全停车需要5秒钟,但是车轮抱死在不到一秒钟的时间内就可能发生了。
防抱死制动系统(ABS)设计有自诊断功能。每当汽车启动时,会进行两项自检。首先,当钥匙打开时,系统进行一项被称为“启动过程”的电器检查。在这项检查中,红色制动警告灯和防抱死警告灯亮。大约1到2秒钟后,测试结束,灯熄灭。当车速达到4.8-6.4千米/小时时,系统进行一项称为“驶离”的功能检查,各液压阀短暂激活,以测试它们的功能。汽车启动后第一次起步时,“驶离”检查可从一系列急速的咯嚓声中被觉察到。如果在“驶离”检查时踩制动踏板,该项检查就不进行了。这两种情况都是系统自检的正常部分。大多数故障将以ABS故障码的形式存储在防抱死制动控制器(CAB)内,它可以通过检索防抱死制动控制器帮助进行故障诊断。



